- For the home
Health
- Bones and Joints
- Digestion and Healthy GI
- Essential Oils
- Fish Oil / Omega-3
- Healthy Sleep
- Heart and Cardiovascular System
- Immunity
- Liver
- MCT Oil
- Men
- Mind and Focus
- Minerals
- Pet Supplements
- Pro-Health Supplements
- Probiotics
- Senior
- Superfoods
- Urinary Tract
- Vitamins
- Vitamins for hair
- Vitamins for nails
- Vitamins for the skin
- Weight Management
- Woman
Healthy Diet
Herbs
Mother and Baby
Sport
Your Goal
Pet Supplements
Cosmetics
- Cosmetics for children
- Men's Cosmetics
- Unisex Cosmetics
- Women's Cosmetics
- Dezodoranty i perfumy
- Higiena jamy ustnej
- Kosmetyki akcesoria
- Kosmetyki dla dzieci2
- Kosmetyki do ciała
- Kosmetyki do higieny intymnej
- Kosmetyki do opalania
- Kosmetyki do pielęgnacji ust
- Kosmetyki do twarzy
- Kosmetyki do włosów
- Papier toaletowy / chusteczki
ForMeds Bicaps Collagen Max (Type II Collagen) 60 vegetable capsules
Available: 30 szt.
27,37 €
Price per portion: 0,91 €Available: 30 szt.
After purchase you will receive 112 pts
Product Details
- Description
- Dosage
- Ingredients Table
- About the brand
- Nutritional information
- Reviews (1)
- Articles
Dietary supplement BICAPS® COLLAGEN MAX contains 40 mg of chicken cartilage (including undenatured type II collagen), 360 mg of L-proline, 100 mg of hyaluronic acid, 100 mg of vitamin C, 100 mg of vitamin K (K2 MK -7) and 50 μg / 2,000 IU of vitamin D (D3) in 2 capsules without any additives.
- Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
- Pullulan is obtained through a natural fermentation process.
- The products do not contain artificial fillers, anti-caking agents and dyes, such as: magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, etc.
- Vegetable container and label
Dietary supplement BICAPS® COLLAGEN MAX supplements the diet with collagen, L-proline and hyaluronic acid.
- L-proline is part of collagen and makes up 30% of the proteins that make it up. (4)
- Hyaluronic acid is present, among others, in the skin and epidermis, connective tissue, cartilage and synovial fluid. (5)
- Vitamin C supports the production of collagen necessary for the proper functioning of bones and cartilage.
- Vitamins K and D help maintain healthy bones. Vitamin D is attending
- in the proper absorption and use of calcium and maintaining its proper level in the blood.
Test results for undenatured type II collagen contained in BICAPS® COLLAGEN MAX:
1. Undenatured type II collagen lowered the biomarker responsible for the deterioration of cartilage. (1)
2. Improvement in quality of life parameters according to the SF-36 questionnaire was noted. He assesses, among others physical, emotional and vitality functioning. (2)
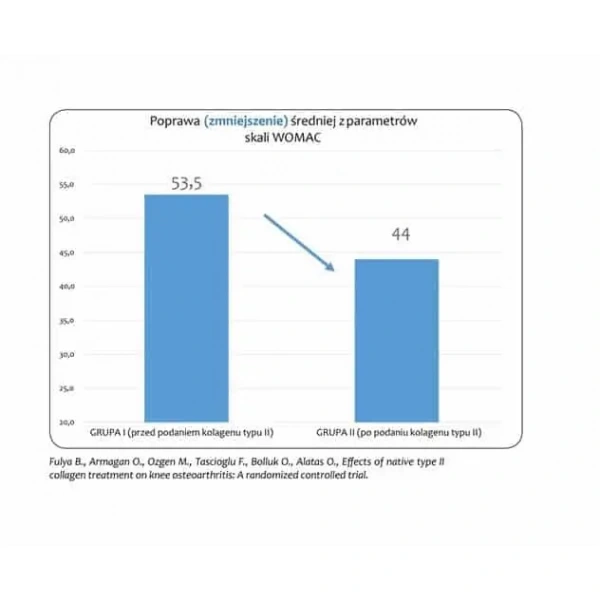
3. The WOMAC scale parameters have improved. The scale assesses pain severity, joint stiffness, and physical function in people with joint problems. (1,2,3)
Sources:
1. Mannelli L., Micheli L., Zanardelli M., Ghelardini C., Low dose native type II collagen prevents pain in a rat osteoarthritis model. Retrieved on 12/05/2018 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3751133/
2. Fulya B., Armagan O., Ozgen M., Tascioglu F., Bolluk O., Alatas O., Effects of native type II collagen treatment on knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4970562/
3. American College of Rheumatology. Retrieved on 2018-05-12 from https://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Rheumatologist/Research/Clinician-Researchers/Western-OntarioMcMaster-Universities-Osteoarthritis-Index-WOMAC
4. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/L-proline#section=Top.
5. Korzeniewska K., Pawlarczyk M., Hyaluronic acid - not only a cosmetic, Farmacja Współczesna 2014; 7: 72-76.
Dosage
Serving Size: 2 Capsules
Servings per Container: 30
Form: Capsule
Other ingredients
Polish manufacturer of supplements without chemical additives that has been successfully operating on the market since 2012. The manufacturer declares that the company's priority is to offer natural, effective and safe products. The proof of safety of ForMeds brand products is the fact that the development of a new recipe and each stage of testing is subject to strict control. A group of qualified and experienced specialists supervises the development of each product. The producer has been awarded many times for quality and efficiency.
Cannot be used as a substitute of a healthy and balanced diet.
Consult your physician if you are pregnant or nursing.
Do not exceed recommended dosage per day.
Keep out of reach of children.
Best before: date on the package
All descriptions are the property of the www.mass-zone.eu. Copying or distribution is strictly prohibited! As per the Copyright Act from February 4th, 1994.
Manufacturer: FORMEDS Sp. z o
Polecam bardzo dobry produkt
We make every effort to ensure that reviews come from customers who have used or purchased the product. Reviews are collected, verified, and published according to the rules described in the store's terms and conditions.