.webp)
.webp)

Martyna Wiśniewska
Vitamin B12 - an essential component of our daily diet
Ten wpis jest dla Ciebie!
VITAMIN B12, WHAT IS IT?
You've probably heard about vitamin B12. Maybe you don't eat meat, or you don't eat much, and someone mentioned that you may be at risk of being deficient in this vitamin. Or maybe you suffer from anemia and the doctor suggested that it may be the result of an improper diet and too low a supply of vitamin B12?
This post is for you!
Vitamin B12 is more precisely cobalamin, a compound belonging to the group of B vitamins. It performs a significant function in the human body, protecting the circulatory and nervous systems. It takes part in the synthesis of serotonin, which as a neurotransmitter is responsible for the mental state of our body. Often serotonin deficiencies can be the cause of vitamin B12 deficiency, contribute to the formation and intensification of depressive states. Vitamin B12 is extremely important in people who train or increase their physical activity, because it is responsible for the production of red blood cells.
The process of vitamin absorption is as follows. The first stage is to cut it off from the proteins in the stomach, this is due to the presence of hydrochloric acid and the protein-digesting enzyme pepsin. The vitamin then binds to the R proteins – haptocorynes so that it can be transported to the intestine. In the intestines, this complex is acted on by proteinases that allow vitamin B12 to detach and combine with Castla factor. Such a complex has the ability to bind to a receptor located in the intestine, and after absorption into the intestinal cell, the complex breaks down and vitamin B12 enters the blood.
CAUSES OF DEFICIENCY
Anemia is the most common cause. The level of homocysteine is also very strongly associated with vitamin B12 deficiency. It is a product formed as a result of the breakdown of proteins. It should be added that this product is not desirable in our body, and excess homocysteine can be the reason for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Again, these can cause a myocardial infarction or stroke.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is quite common, but what could be the causes? Often, intestinal diseases, and thus poor bacterial flora, can cause problems with the storage and absorption of vitamin B12. Another example may be a problem with too high pH (alkaline) in the stomach, which causes a shortage of gastric juices, and these secondary problems with the flora and vitamin B12 deficiency.
Also obese people who have undergone bariatric surgery are at particular risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. Due to this operation, the area of absorption is much smaller, and the residence time of food in the digestive tract is much shorter. This may result in insufficient digestion by enzymes of the eaten food.
Autoimmune diseases as well as hypothyroidism can also cause vitamin B12 deficiency.
DEFICIENCY SYMPTOMS
Have you noticed any strange symptoms?
Do you get tired more often?
Having trouble concentrating?
Be sure to do blood tests, consult a specialist, because these may be symptoms of vitamin b12 deficiency. Particularly vulnerable to deficiencies are people on a vegan or vegetarian diet, the elderly. If you are after gastric resection surgery, you should also consider supplementing with this vitamin. Absorption problems are common after gastric surgery. Similarly, if you suffer from celiac disease or suspect problems with the assimilation of minerals and vitamins, check-ups should be performed and a diet and supplementation should be started in case of deficiency. In people who are chronically ill with Crohn's disease, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, we can expect vitamin b12 deficiency.
According to the results of research conducted by scientists, vitamin B12 deficiency may contribute to the development of Alzheimer's disease. Sufferers very often suffer from elevated homocysteine levels, which, as you already know, can be an indicator of vitamin B12 deficiency.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, perform the tests and consult a specialist.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency initially may be confused with other diseases. You should be concerned if you have recently noticed fatigue, lethargy, fatigue, shortness of breath, accelerated heart rate.
- A deficiency may be taste, smooth shiny “buffalo tongue” manifested by a burning tongue, aversion to meat and fried products, weight loss, constipation, nausea and diarrhea.
- Common in people with deficiency of vitamin B12, pallor of the skin is noticeable, the so-called zajady located in the corners of the mouth, headaches and dizziness. Problems with acne, rashes, hair loss are also a signal to test the level of vitamin B12.
- You already know that vitamin B12 has a huge impact on the nervous system, its deficiency can result in tingling of the lower and upper limbs, loss of deep sensation, problems with gait stability, vision impairment.
- Our psyche can also give signals that we may not associate with vitamin B12 deficiency and ignore.
To them include: depressive disorders, states of increased arousal, changes in behavior, memory disorders and even dementia. A noticeable growth retardation in children can also be caused by a deficiency of this vitamin. Children diagnosed with autism very often have problems with a varied diet, therefore they may also be deficient in this vitamin.
CAN YOU OVERDOSE VITAMIN B12?
Not really, but use supplementation in excess, not properly washed, without the supervision of a specialist, may lead to an allergic reaction to vitamin b12. However, this vitamin, due to its solubility in water, is not accumulated, and its excess is excreted with sweat and urine.
VITAMIN B12 IN DAILY DIET
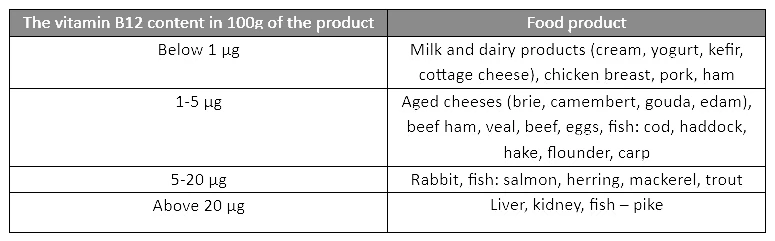
The most of this vitamin you will find in products of animal origin such as eggs, milk, dairy products and meat, especially offal. This is because the production of the vitamin is carried out by bacteria living in the digestive system of animals.
Non-animal sources include food yeast and fermented soybeans in the form of thick miso paste, as well as mushrooms. A large number of products specially designed for people on a vegetarian diet are fortified with vitamin B12, such as breakfast cereals.
In addition, it is observed that vegetable preserves containing lactic acid, such as sauerkraut and pickled cucumbers, contain trace amounts of vitamin B12. Due to the beneficial effect of fermented products on the intestinal flora, it is recommended to include them in the diet as much as possible.
HOW TO SUPPLEMENT?
What to do to avoid lead to shortages? First of all, diversify your diet with products rich in vitamin B12, but if you suffer from intestinal diseases or other diseases that prevent you from providing the right dose of vitamin from food, you should contact a specialist regarding supplementation.
The daily requirement for healthy people without deficiencies is:
2 micrograms for an adult, 2.2 micrograms for a pregnant woman and 2.6 for a nursing woman.
However, if you decide to take supplementation, remember about a few rules so that supplementation is effective and the absorption of vitamin B12 is as high as possible. It is recommended to supplement, in addition to vitamin B12, also folic acid. If you have vitamin C in the recommended supplementation, remember that the interval between taking vitamin C and vitamin B12 should be at least an hour. All stimulants should be eliminated, they have a very bad effect on the intestinal absorption process, preventing the penetration of active compounds into the intestinal cells.
WHICH PRODUCT TO CHOOSE?
The most important thing is that the dose should be higher than the daily requirement, the tablet should also have a homocysteine-lowering effect . High homocysteine is not only a deficiency of vitamin B12, but also B6, biotin and folic acid. So it's good to choose a preparation containing all these ingredients right away. The form in which we take supplementation is also important. The most absorbable form of vitamin B12 is methylcobalamin.
SOME RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS BELOW:
Doctor's Best Chewable Fully Active B12
A form of methylcobalamin. 1 tablet contains 500 mcg.

Vitamin B12 - Jarrow Formulas Methyl b12
Here, too, we have the methylated form available. 1 tablet contains 100 cmg of vitamin B12.

For greater deficiencies, this product is recommended:
JARROW FORMULAS Methyl B-12 2500mcg 100 pills
The methylated form of vitamin b12, but one tablet contains as much as 2500mcg
The largest amount available in tablets can be found in this Natrol product:
NATROL Vitamin B-12 Fast Dissolve 5000mcg - 100 tablets
Vitamin B12 is provided in the form of cyancobalmin and one capsule contains 5000mcg

Complex of B vitamins - Doctor' ;s Best Fully Active B-Complex - 30 caps.
In this product, in addition to methylcobalamin, we will find a whole group of B vitamins, including vitamin B3 - niacin, vitamin B1 - thiamine, biotin, vitamin b8, vitamin b2, and our vitamin B12, also in the form of methylcobalmine. 1 capsule contains 1000 mcg of vitamin B12
In addition to diet, supplementation with tablets, the most serious forms of deficiency are often treated with injections of vitamin B12. They are administered intramuscularly, however, the multitude of side effects forces you to consider the legitimacy of this form of supplementation and use it only in chronic weakness of the body caused by vitamin B12 deficiency.
Kośmider A, Czaczyk K, Vitamin B12-structure, biosynthesis, functions and determination methods., Food. Science. Technology and Quality., 2010, 5(72)
Gawęcki J. Vitamins, collective work, Library of the Nutrition Knowledge Olympics, 2000
Zabrocka J, Wojszel Z, Vitamin B12 deficiency in the elderly - causes, consequences, therapeutic approach, Geriatrics 2013, 7
Rate the text

Martyna Wiśniewska
As a dietitian, she assists in clinical dietotherapy, helping patients not only lose weight but also feel better in their bodies. In her office, she sees patients whom she helps in the treatment of diet-dependent diseases such as diabetes, insulin resistance, hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, as well as in the therapy of allergies and food intolerances, and diet therapy for diseases such as celiac disease, Hashimoto's disease, Crohn's disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and thyroid diseases. Patients who suffer from eating disorders, depression, sleep problems, chronic stress, or simply want to have more energy in life can rely on her professional help.
As a dietitian, she assists in clinical dietotherapy, helping patients not only lose weight but also feel better in their bodies. In her office, she sees patients whom she helps in the treatment of diet-dependent diseases such as diabetes, insulin resistance, hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, as well as in the therapy of allergies and food intolerances, and diet therapy for diseases such as celiac disease, Hashimoto's disease, Crohn's disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and thyroid diseases. Patients who suffer from eating disorders, depression, sleep problems, chronic stress, or simply want to have more energy in life can rely on her professional help.









.png)

















